Java remains the second-most popular coding language in the world according to the PYPL Index, and it ranks third among skilled professionals to develop high-performance applications across multiple platforms — only C and Python score higher.

As a result, you’ll often find Java running in the background of many Mac or Windows systems. However, if the version of Java you have isn’t up to date, applications may not work as intended — or may refuse to open at all.
In this piece, we’ll walk you through how to check your Java version in Mac and Windows to make sure the Java you’ve got is the one you need.
How to Check Your Java Version
When it comes to Windows, there are two easy ways to check your Java version:
If you’re a Mac user, you’ve also got two simple options:
Let’s break down each method in more detail.
How to Check Java Version in Windows
1. Check the Java Version Using the Control Panel
If you’re a Windows user, the Control Panel approach is quick and easy.
First, click on the magnifying glass icon at the bottom-left of your desktop.
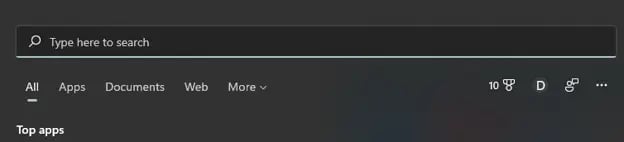
Next, type in “About Java” in the search bar that appears, then click on the “About Java” app that appears. If it doesn’t come up, try “Configure Java”. If you’re still having no luck, you probably don’t have Java installed.
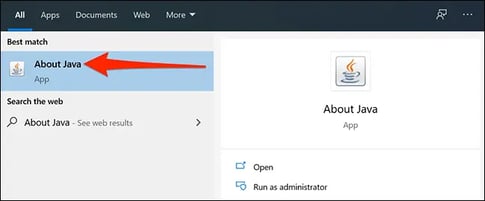
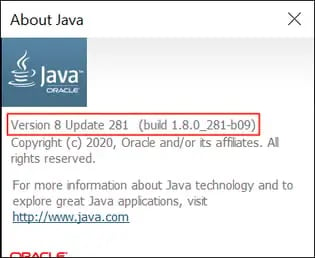
Once you click through on About Java or Configure Java, you’ll see a pop-up window indicating the current version and build number.
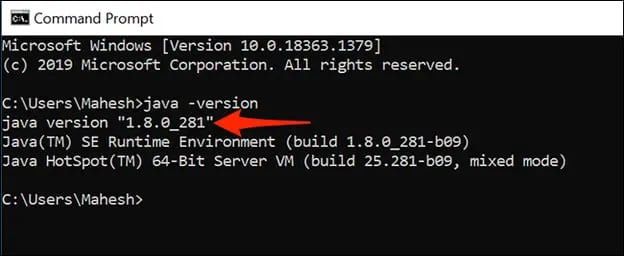
2. Check the Java Version Using the Command Line
You can also check your Java version in Windows using the command line.
First, click on the magnifying glass and type “cmd”, then click on the Command Line app icon that appears.
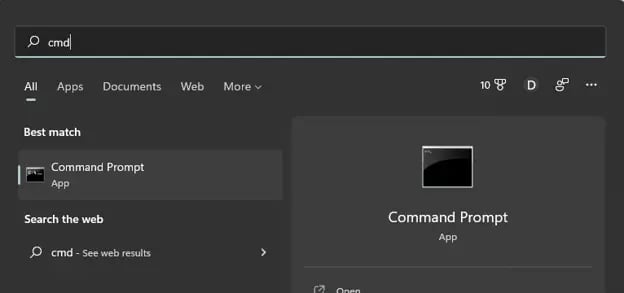
Now, enter the command java -version and you’ll see the version of Java listed.
The video below not only covers these two common methods but an additional third method as well.
How to Check Java Version in Mac
1. Check the Java Version Using System Preferences
To check your Java version on a Mac without leaving the GUI, start by clicking the Apple icon in the top left-hand corner of your screen, then select “System Preferences.”
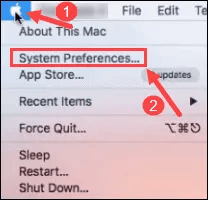
Next, find and click on the Java icon in the list of programs shown.
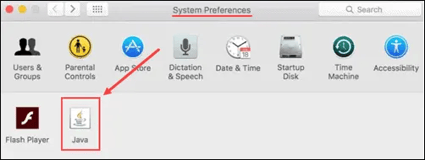
Finally, click on the “About” button to see the version of Java you’re currently running.
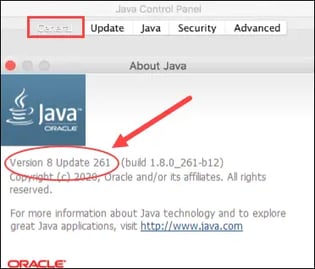
2. Check the Java Version Using the Terminal
Checking your Java version on Mac using the terminal is similar to using the Windows command line.
First, find and click on the spotlight search bar in the top-right corner of your screen, then type in “terminal” and click on the terminal icon.
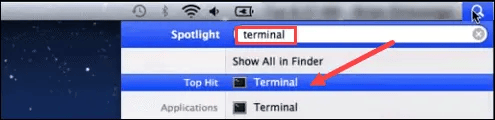
This will bring up the command line. From here, you enter the same command as in Windows, java -version to get your current version details.
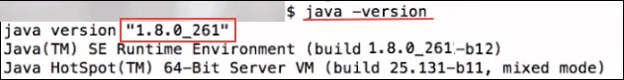
Worth noting? On both Windows and Mac devices, you can use the command javac -version to check the version of your primary Java compiler. This video can show you how:
Checking Your Java Version
And there you have it: Four simple ways to quickly check your Java version and make sure you’ve got the newest, freshest Java served up and ready to go.




![How to Build & Run an Effective Website With a Small Team or Budget [Startup Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/website-on-a-budget.jpg)



![How to Make a Website With User Accounts and Profiles [With WordPress, Wix, and More]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-create-user-accounts-and-profiles.jpeg)

