Humans have an inherent negative bias, meaning we tend to register negative stimuli more readily and dwell on those experiences more often. The same phenomenon applies to customers and their pain points.

Although it is important to talk about all the benefits and outstanding features of your product, customers are more likely to move toward a purchase decision if they feel your product can alleviate the discomfort of their persistent pain points.
By identifying and addressing customer pain points in your marketing and sales efforts, you can create a more compelling strategy that will make your company invaluable in the eyes of your customers.
- What are pain points?
- How to Identify Customer Pain Points
- Pain Point Examples
- Customer Pain Points
- Business Pain Point Examples
- 4 Tips for Addressing Business Pain
What are pain points?
Pain points are persistent problems with a product or service that can inconvenience customers and their businesses. Or to simply put it, they’re unmet needs waiting to be satisfied.
Customer pain can be related to their personal or professional lives and can be physical, emotional, or logistical.
Some prospects may not even be aware of the pain points they are experiencing. You must convince them they have a problem and that your company has the solution to fix it.
.png)
Free Guide: 101 Sales Qualification Questions
101 Questions to Ask Contacts When Qualifying, Closing, Negotiating, and Upselling.
- Budget Questions
- Business Impact Questions
- Competitor Questions
- And More!
Download Free
All fields are required.
.png)
How to Identify Customer Pain Points
We know that pain points are problems that customers and prospects experience, but how do you identify them?
Pain points can be as diverse and unique as the people who experience them, so it’s important to conduct qualitative research to uncover the nature of your customer’s pain points. Only then can you understand where you fit in to fix them.
Here are some steps to discover those pain points.

1. Engage with customers.
The best way to discover your customer’s pain points is to let them tell you directly. Conduct customer research, such as surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
By asking targeted questions and listening intently to customer responses, you can better understand and solve their problems. You should also implement live chat on your site so customers and prospects can contact you with questions and issues.
2. Ask your sales team.
Your company’s sales team speaks with prospects and customers regularly. They’re a valuable source of information on your customers’ persistent pain points and how you can step up to solve them.
Your sales team will also have a different perspective on customer pain points that can help you discover underlying trends and even pain points unknown to some customers.
However, you should be wary to ensure you are differentiating between customer pain points and pain points your sales team may be experiencing if they are having difficulty closing deals.
3. Analyze customer feedback.
Your customers and potential customers are likely airing out their pain points online. If you know where to look, you can turn those areas of discomfort into powerful selling points for your business.
Analyze your customer support tickets to learn about your customers’ pain points, and keep an ear out on social media and online reviews to find out where people in your industry are feeling pain. Consider social listening software to help with this task.
Looking for more info on how to identify customer pain points? Check out the video below.
Pain Point Examples
We’ll break down more specific scenarios further in this article, but for starters, here are a few general types of pain points you may come across.
- A customer needs a service above their budget. Financial limitations stop customers from working efficiently and lead them to search for more cost-effective alternatives.
- A business with too many redundant steps in its strategy. Too much process lead time costs money and reveals a need to reduce it.
- Unclear communication between departments. Teams need to find a way to communicate information properly to reduce errors in the process.
These are all situations that cause “pain" or stifle productivity. The first step in addressing these pains is knowing how to identify and eliminate them, so let’s discuss how to do it for your customers.
Addressing Customer Pain Points
Whether it’s a complaint about customer service, dissatisfaction with a product or service, or an idea for an innovation that you have yet to discover — your customer can fill you in.
There are many different ways to identify and treat customer pain points. The best way to do it is to hear what they have to say.
Customers are your bread and butter. They’re a priority whether they purchase an end product or a service to help run their operations. So now let's segue into what it means to have pain points as a business.
Pain Points in Business
Business pain points are problems causing 'pain' in an organization, and you can provide the solution. Real business pain isn’t a problem where the solution is a nice-to-have. It’s a budgeted, have-to-get-it-solved, discussed-at-the-board-level kind of problem.
Because they affect the bottom line, businesses must solve them for the organization to function successfully. Business pain points keep the company from functioning and must be addressed urgently.
Business Pain Point Examples
Business pain points are issues that affect a business’s bottom line severely, and there’s a lot more where that came from.
Pain is the first thing top salespeople look for in their prospects because pain starts potential customers on their buyer’s journey to find a solution.
Here are the most common types of business pain points your prospects might be facing, along with examples of each.
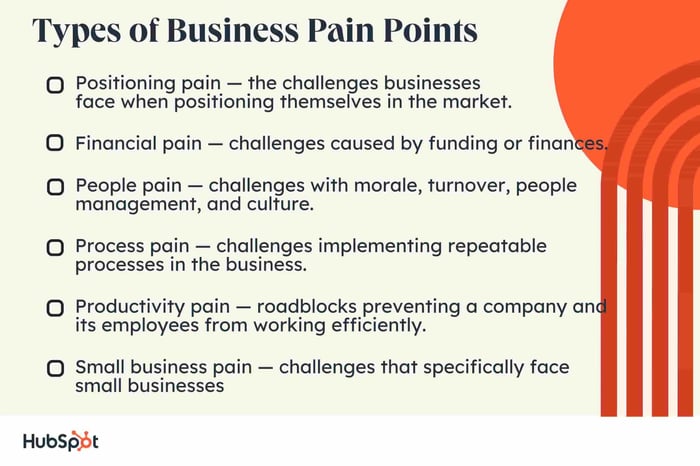
1. Positioning Pain Points
Positioning pain refers to the challenges businesses face in positioning themselves in the market. These pain points can arise when businesses struggle to differentiate themselves from competitors or to reach and connect with their target audience.
Here are some examples of what you might hear from prospects who have positioning pains:
- “No one knows who our company is."
- “Our competitors are outspending us."
- “The market is changing, leaving us behind."
- “Until now, we haven’t considered digital marketing, so we’re behind."
- “Our competitor has more green space on most channels."
Suppose you can identify prospects experiencing positioning pain and offer them a solution for creating a niche and making them known to customers. In that case, your product or service is sure to be valuable in their eyes.
2. Financial Pain Points
Business is all about money. Not having enough of it is a problem, and most difficulties become more manageable when you have more. Every company benefits from improving its financial standing.
Here are some examples of financial pain points that require serious solutions:
- “We’re not selling enough to keep the lights on."
- “Revenue is up, but profitability is low."
- “We don’t have enough visibility to know if we’re making good financial decisions."
- “We may be overpaying for equipment and tools, but we don’t know what to cut."
- “We have signups, but they bounce."
When working with prospects experiencing financial pain points, emphasizing your lower price point (if applicable) will help. If your solutions can help manage cash flow and reduce spending, you may have luck with prospects feeling this variety of business pain.
3. People Pain Points
People are at the heart of every business, often constituting any organization's greatest expense and most significant asset.
If there are people problems such as the following, it can cause issues in other areas of the business:
- “Employee morale is low."
- "We lose our best employees to higher paying positions elsewhere."
- “Our lack of diversity leads to lack of innovation."
- “We can’t trust our middle managers to train and motivate."
- “Our actual company culture doesn’t align with what we declared."
If your product or service helps organizations manage, incentivize, or delight employees, you’ll be a hero, and the sale will be a done deal.
.png)
Free Guide: 101 Sales Qualification Questions
101 Questions to Ask Contacts When Qualifying, Closing, Negotiating, and Upselling.
- Budget Questions
- Business Impact Questions
- Competitor Questions
- And More!
Download Free
All fields are required.
.png)
4. Process Pain Points
With people problems come operational problems (or the other way around). Your prospects know the best way to achieve repeatable success is by implementing repeatable processes. The question is, “how?"
They may be facing hurdles such as:
- “Our hiring process is unwieldy, and we struggle with finding highly qualified candidates."
- “Customer churn is high because our service department is inundated and can’t keep up."
- “We have no system in place to qualify leads."
- “There are inconsistencies in each employee’s workflow, which leads to disorganization and varying performance."
- “The current software we operate in is outdated, but we fear transitioning to a new one will be hard."
If you unearth process pain points, ask your prospect to envision what a smoothly running company, department, or system would feel like and what kind of difference it would make.
5. Productivity Pain Points
A manager’s job is to remove roadblocks for the team so that things get done, productivity remains high, and profits increase. That said, it’s easy to get stuck in the weeds of the business and fall victim to time-wasting inefficiencies.
Here are some examples of productivity pain points in business:
- “We keep missing client deadlines."
- “We spend way too much time in meetings."
- “Our administrative work is out of hand."
- “Quality issues with our product have led to costly recalls and customer churn."
- “Our employees aren’t supported enough to complete their assigned tasks."
If something prohibits a company and its employees from working efficiently, you can position your solution as a time, money, and headache saver.
6. Small Business Pain Points
Pain points left unsolved when working in a small business can potentially halt operations altogether.
If your customer is a small business, you need to ask questions addressing the many tasks a small team has to complete, unlike a large corporation where people don’t need to wear as many hats.
Some examples of small business pain points are as follows:
- “Orders consistently ship late, and our team is already so stressed trying to keep up."
- “Sourcing talent best fit for the business hasn’t been easy."
- “Posting across all of our social media channels is tedious."
- “In my business, managing a team is intimidating because I already wear many hats."
- “Keeping up with accounting grows more complicated as time progresses."
Many of these issues can be addressed with a product or service offering grounded in current technology and consulting. Small businesses could benefit from workflow automation and proper guidance from experienced professionals.
4 Tips for Addressing Business Pain
Once you identify pain, you can determine how to solve it for your prospect. Business pain points are an incredible tool to leverage as a salesperson. You can become a solution provider rather than a product seller.
Here are four tips to start positioning in this way.

1. Use your prospect’s language when talking about pain.
This psychological technique can go a long way in building trust with your prospect. Instead of trying to appear impressive by relying on jargon only your colleagues would understand, show your prospect you take them seriously by leveling with them and using their language and terminology.
2. Find out who’s empowered to solve the pain.
Find the economic buyer as quickly as possible. Ask your prospect whose budget a purchase would come out of and what teams need to be involved in a buying decision.
There’s little point in spending hours with someone who can’t ink a deal.
3. Identify additional key stakeholders as early as possible.
If you’re selling to multiple teams and one team has completely different priorities than another, you need to know early on. If you have to go through a two-month legal review process before you can close a deal, you also need to know in advance.
Prospects are sometimes worried they’ll appear less authoritative if they tell you they’re not the sole decision-maker, so I like to use the following questions to avoid that impression:
- Who besides yourself needs to be involved in this decision?
- Who else would want to know that we had this conversation?
4. Frame your offering to reflect the prospect’s dilemma.
As you build trust with the prospect and listen to different perspectives, you must personalize the solution to their specific needs. For example, tell them which features solve their problems if your product serves multiple purposes.
Listen and affirm your prospect’s pain points while asking for information. It’ll be easier to make your pitch meet everybody’s requirements.
Understanding Pain Points
Inbound sales is all about empathy. To close more deals and become as helpful as possible, start asking the right questions to the right prospects. Soon, you’ll know their biggest challenges and how you can offer a solution.
![Free Download: 101 Sales Qualification Questions [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/e97d6603-b40e-4085-ad55-0074b7351ead.png)

![How to Use BANT to Qualify Prospects in 2024 [Expert Tips]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/bant-questions-6606f7b6c0d9e.webp)



![21 Signs Your Buyer Is a Poor Fit [Sales Process Checklist], According to HubSpot's Former Sales Director](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/Bad%20fit%20checklist.jpg)